Research on the development of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology Text / Yin Yiguo Volatile organic waste gas (hereinafter referred to as VOCs) is a harmful gas whose boiling point is close to the boiling point of water. Some boiling points of VOCs are at higher temperatures. At this time, the saturated vapor pressure of these organic waste gases will be higher than 133.3Pa. Under such conditions, they may become volatile organic compounds, which can pollute the air and affect human health. The main components of these volatile organic compounds include: polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons such as sulfur hydrocarbons, oxygenated hydrocarbons, nitrogen hydrocarbons, halogenated hydrocarbons, hydrocarbons, etc., because of their similar properties, they are easily mixed together and pollute the environment. These VOCs can also threaten the health of human beings, enter the human body in people's breath, and cause damage to human organs. Therefore, in the era of technology, volatile organic waste gas must be treated to control organic waste gas at a certain concentration. 1 Analysis of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology In the high-tech era, the surface of many high-tech products uses paint, plastics, chemicals, and other chemical materials, and many organic substances are used for processing. When these organic substances are used, they will form many volatile organic waste gases. They not only cause physical harm to workers, but also if these gases are arbitrarily discharged into the air without treatment, they will pollute the environment and cause serious harm to human health. For common VOCs treatment technologies, the following are available. Several. 1.1 Treatment of volatile organic waste gas by combustion The combustion method utilizes the flammability of VOCs. Since they can burn themselves, if these organic substances are passed to an incinerator at a certain temperature, these organic substances can be burned. When these organic substances generate CO2 and H2O, They can be discharged into the air. The treatment mechanism of this combustion method is mainly divided into three forms: direct combustion method, thermal combustion method and catalytic combustion method, depending on the combustion temperature and the combustion mode. 1.1.1 Treatment of volatile organic waste gas by direct combustion Direct combustion is the direct combustion of VOCs by directing VOCs directly into the incinerator to allow VOCs to burn at high temperatures. If the concentration of VOCs is high, they can be burned well in the furnace to generate CO2 and H2O. When the concentration of VOCs is low, the combustion at this time is insufficient, so it is necessary to take certain measures, such as adding auxiliary fuel. The VOCs are completely burned, and finally the VOCs are completely formed into CO2 and H2O, and these CO2 and H2O can be exhausted. The advantage of this method is that due to their low investment cost, the equipment to be prepared is relatively simple and convenient in operation, but the method of using this combustion needs to maintain the condition of high temperature combustion (>1100~C), and at the same time, Under such high temperature conditions, it is easy for the product to form NOx compounds which cause secondary pollutants in the combustion. 1.1.2 Treatment of volatile organic waste gas by catalytic combustion The catalytic combustion method is a method in which a catalyst is added to a reaction system to completely react VOCs under the action of a catalyst to form CO2 and H2O, and then discharge them into the air. The mechanism of action of this catalyst is mainly to reduce the ignition point of VOCs. There are many types of such catalysts currently used, and these catalysts are mainly noble metal catalysts (such as Pt, Pd) and non-precious metal catalysts (woman mouth V, Ti, Fe, Cu, etc.). Catalyst Pt/H-Beta and PdO/H-Beta and other catalysts, when they are in contact with VOCs, have strong selectivity for chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as Pt/H-Beta and PdO/H-Beta. Catalysts are easy to cause them to undergo catalytic decomposition]. The study by MACenteno_3 et al. shows that the catalytic combustion method can make the Au/TiOxNy catalyst highly catalyzed by organic substances such as hexane, benzene and propanol. Under this catalysis, the VOCs are completely burned. If the catalytic combustion method is compared with the thermal combustion method, they each have different advantages, but the combustion temperature required for the catalytic combustion method is lower (200 ° C ~ 400 q C), which is its advantage. Since they can be burned at lower temperatures, the generation of secondary secondary pollutants can be avoided and the environment can be protected. However, the catalysts currently used, due to their unstable properties, are easily destroyed by substances containing s, P, As, etc. under certain conditions. Once the activity of the catalyst is destroyed, the catalyst is deactivated, if the catalyst is inactivated, As long as the reaction is carried out, the catalyst needs to be replaced, and this process also requires an expensive cost. 1.1.3 Treatment of volatile organic waste gas by biological method Biological filtration treatment of VOCs, this organic waste gas, is mainly the main source of industrial production, municipal sewage, sludge treatment. In order to control malodorous gases, a biofiltration method has been proposed. In recent years, with the development of science, it has been found that this treatment method has a good effect on the treatment of VOCs. This biological filtration method can process lower concentrations of VOCs, the core processing equipment is the role of the biological filter bed (as shown in Figure 1), VOCs can be processed in the biological filter bed, so that VOCs generate CO: and HO, which Mainly due to the fact that in the filter bed, there are already fillers capable of forming biofilms, which can cause VOCs to be adsorbed by biofilms in the filter bed, decompose VOCs into CO2 and H2O, and discharge them to the air. It is purified. This biological filtration method determines the efficiency of its treatment efficiency, mainly the control of the biological filtration operating conditions. Therefore, when this method is used, good results can be obtained by controlling the operating conditions. This method can be achieved by controlling the results of different organic substances, which can reach 40% to 98%. The biological filtration method has a low operating cost, which is beneficial to the application of the enterprise, but because of the large equipment of this method, and its selectivity for processing VOCs, this weakens the scope of use of this method. 1.1.4 Treatment of volatile organic waste gas by adsorption The adsorption method utilizes an adsorbent having a microporous structure, and the method uses the adsorbent to adsorb the adsorbate in the air on the surface of the adsorbent, and the organic matter is separated from the main body by adsorption of the adsorbent, so that It is possible to treat organic waste gas. The adsorption process is shown in Figure 2. When the VOCs pass through the action of the fan, they are transported to the adsorption tower 1. When the adsorption tower 1 reaches the adsorption saturation, the valve can be closed and the VOCs gas can be switched to the adsorption tower 2. Adsorption, since VOCs are desorbed in column 1 and column 2, respectively, they operate alternately with each other. Therefore, as long as the design is reasonable, the results of continuous treatment can be achieved, and the VOCs can be purified. At present, the commonly used adsorbent: due to the better performance of activated carbon, this is mainly because the activated carbon has a large specific surface area, which makes the activated carbon have a higher adsorption capacity, so that VOCs are larger; another method is zeolite molecular sieve, The adsorbent has a uniform microporous structure, which makes the microstructure more selective. It can make them have a big advantage. In the process of adsorbing VOCs, they all have higher removal efficiency, so that they can achieve the effect of adsorbing VOCs, and because of their low energy consumption and mature process, therefore, The methods are easy to promote and practical in general enterprises to process VOCs for purification. It should be pointed out that there are still gaps in the processing of VOCs in China. The above treatment methods are only suitable for high- and medium-concentration VOCs treatment, but these methods are relatively weak for low-concentration VOCs. In such an environment, it will affect the human respiratory system, causing the nose, eyes, heart, liver, lungs and other organs to be harmed by harmful gases. Living in this organic exhaust gas for a long time will lead to the human body. Allergic reactions occur in organs, and humans take a long time to inhale organic waste gas; it can cause inhalation and carcinogenicity of inhalers, causing irreparable harm to humans. Therefore, for the research and innovation of Chinese VOCs governance technology, at present, science and technology workers are actively introducing or developing new technical methods, so as to ensure that China's environment is excellent, in order to avoid harm to human health caused by VOCs. 2 Progress and application of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology 2.1 Microwave catalytic oxidation technology and its application in the treatment of volatile organic waste gas Microwave catalytic oxidation technology is a high-tech processing technology. With the development of science, this technology has been developed at a high speed. It can effectively combine traditional filler adsorption technology to improve the ability to deal with VOCs. It has changed the transformation of the traditional desorption treatment method to the microwave desorption treatment method, which greatly improved the treatment effect. In the process of controlling VOCs, using microwave catalytic oxidation technology, it can not only shorten the desorption and adsorption time of exhaust gas, but also use this technology to reduce the consumption and waste of various energy sources, reduce processing costs, and improve the treatment ability of VOCs. The adsorbents currently used can be used continuously for twenty times, and these adsorbents can achieve very good adsorption effects during repeated use, and the VOCs are thoroughly treated. 2.2 Activated carbon fiber treatment technology and its application in the treatment of volatile organic waste gas Activated carbon fiber treatment technology is an innovation in the high-tech era. Compared with the traditional carbon adsorption technology, this technology has better adsorption performance in terms of performance. The principle of this VOCs treatment technology is: because of its high-adsorption property through the addition of activated carbon fiber, due to its high-efficiency adsorption, it is mainly due to the activated carbon fiber with environmentally friendly materials, thus making its inner surface and outer A large number of carbon atoms are distributed on the surface, and due to the action of these carbon atoms, these carbon atoms constitute a surface structure having a strong adsorption capacity. The surface structure of this activated carbon fiber has a strong advantage. In order to compare the performance of the two, that is, the adsorption performance of the activated carbon fiber and the conventional carbon adsorption material, it is confirmed by experimental results that due to the special structure of the activated carbon fiber, the adsorption result is more advantageous, so that it can make Activated carbon fiber has excellent performance, and has many advantages such as fast adsorption speed, large adsorption capacity, easy regeneration, large surface area, abundant micropores and high carbon content. These numerous advantages can make them in the process of treating VOCs. Fully exerting the effect of adsorbing VOCs can show that the activated carbon fiber has a very good effect. Therefore, the activated carbon fiber treatment technology has great advantages. It is very suitable for extensive promotion and application in the governance of VOCs, making the environment more fresh. 2.3 Bioremediation technology and its application in the treatment of volatile organic waste gases Bioremediation technology is a relatively new method in the management of VOCs. The main application principle is that through the development of bioremediation technology, the microbial degradation process can be used to treat these VOCs organic matter and transform them into Inorganic substances such as water and carbon dioxide, so that the organic waste gas polluting the environment is disposed of. However, due to the complexity of the bioremediation technology for the treatment of VOCs, it is difficult to ensure that no harmful substances are produced in the gas phase in bioremediation technology, which will affect the results of bioremediation techniques. Therefore, in practical applications, attention should be paid to ensuring The liquefaction of gaseous pollutants, after the liquefaction of gaseous VOCs pollutants, requires the liquefaction process of biosorption, metabolism and degradation of various pollutants. However, this treatment method has not yet formed a perfect theory, and no suitable method has been found in practical applications. Therefore, in order to utilize biotechnology to process VOCs, many scientific and technological workers need to continue their efforts to further in-depth research. 2.4 Nanomaterial purification technology and its application in the treatment of volatile organic waste gas Nanomaterial purification technology is a new technology for processing VOCs in recent years. Nanomaterials refer to ultra-fine materials. The nano-particles of this ultra-fine material have a very high adsorption capacity due to their large surface area. Therefore, nano-materials can exhibit very good catalytic effects during the reaction. In the process of processing VOCs, the reaction rate of VOCs decomposition can be effectively improved due to the addition of nanoparticles, which has great advantages for the treatment of volatile organic waste gas, and even can not be reacted. Substances can also make them complete. Obviously, nano-TiO has advantages in the treatment of gaseous organic pollutants. These advantages are mainly due to their ability to activate nanomaterials under light conditions, which can make nano-TiO: convert organic matter into small molecules such as organic acids, water, carbon dioxide, etc., thus disposing of contaminated organic matter, apparently, nano-TiO The photocatalyst has a great advantage in the treatment of VOCs. It has great advantages in the degradation of VOCs and has great ability to purify air. Therefore, it can make nano-TiO: very Wide application prospects. For better analysis and comparison, the analysis and comparison results of the above-mentioned several VOCs treatment process characteristics are given in Table 1, and the comparison can be clearly made. Table 1 Analysis and comparison data table of several organic waste gas treatment process characteristics Operating expenses Processing efficiency /% Advantages and operational effects Disadvantage Thermal combustion Higher 95~99 High efficiency and good heat recovery The secondary pollutants produced need further treatment Catalytic combustion Higher 90~98 High efficiency, better recovery of heat Strict operating conditions; due to the easy use of catalyst poisoning in some substances, the production of secondary pollutants needs further treatment Biological filtration low 60~95 Low investment costs and no secondary pollution Long processing cycle; mixed biological cultivation is difficult; resources cannot be recycled Condensation high 70~85 Recycling resources are better Operating conditions are harsh, requiring organic matter boiling point not to exceed 33 ° C Absorption (different) high 90~98 Simple equipment, easy maintenance and good results - Absorbent low 80~90 High efficiency, high elasticity and good effect High operating costs, additional costs for the handling of the absorbing liquid Adsorption low 90~96 Adsorbent can be recycled better The adsorbent bed is easily blocked and the treatment efficiency is affected by temperature and humidity. Membrane separation high 90~98 Recycling resources are better High investment cost, difficult to clean the filter membrane 3 Conclusion China has invested a certain amount of energy in the research of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology. At present, there are many types of development and application. They are microwave catalytic oxidation technology, activated carbon fiber treatment technology, biological treatment technology, nano material purification technology, and membrane-based absorption. Purification technology, etc. These technologies have been widely used in practice, and have achieved good results, especially in the process of processing VOCs, can effectively overcome the drawbacks of traditional VOCs governance technology. In order to better manage VOCs, in the future application, different governance technologies can be utilized to make them use different characteristics to make them better handle VOCs. Therefore, in the actual work in the future, according to the actual situation of specific VOCs, Choosing the appropriate governance technology, in order to deal with the removal of VOCs, can ensure the effectiveness of VOCs in the environment and ensure the sustainable development of the environment. Best High Chair,Portable High Chair,High Chair,Wooden High Chair NINGBO BABY FIRST BABY PRODUCTS CO.,LTD. , https://www.maxinfglobal.com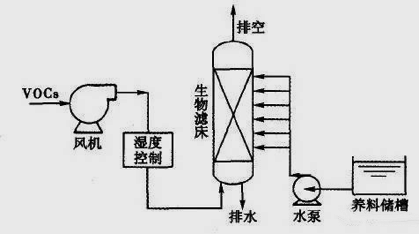
Figure 1 Flow chart of the biological filtration process 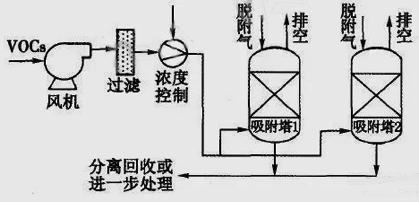
Figure 2 adsorption process flow chart
Research on the development of volatile organic waste gas treatment technology