Problems Needing Attention in Spray Painting Process and Equipment Design of Waterborne Coatings Wen/Ma Chunqing Abstract: This paper introduces the characteristics of waterborne coatings, and discusses some major issues that need to be paid attention to in the spray process and equipment design. Keywords: waterborne coating; spraying process; equipment design 1 Introduction With the development of the paint industry, the paint has more and more colors, varieties, and functions, and the division of labor is getting more and more detailed. However, due to the large amount of organic solvents discharged during the manufacture and construction of paints, the environment is greatly polluted. In order to limit the emission of organic solvents, coatings have become increasingly solid, solvent-free, and water-based. Among them, the water-based coating is a very rapid development in recent years, but due to water-based paint and solvent-based coatings, there are many differences: water-based paint with water as a diluent, solvent-based paint with toluene, xylene, acetate Ester and other organic solvents are thinners; In the spraying process and equipment design, we need to fully understand the characteristics of water-based paint, according to its characteristics to design a scientific and reasonable spraying process and equipment. 2 Characteristics of Waterborne Coatings Water-based paints have the characteristics of low volatility, high surface tension, high electrical conductivity, corrosiveness, and easy to generate air bubbles compared with solvent-based paints, resulting in water-based paints that differ from solvent paints in terms of construction equipment and processes. The main solvents used for waterborne coatings are compared with the characteristics of some commonly used solvents used in solventborne coatings. Table 1 Comparison of Main Characteristics of Water and Common Solvents Water volatilization in waterborne coatings is controlled primarily by the temperature and humidity of the spray booth. Solventborne coatings can adjust solids content by adjusting the volatilization rate of the diluent. The solid content of the water-based paint is usually 20% to 30%, and the solid content of the solvent-based paint is as high as 60% to 70%, so the smoothness of the water-based paint is good. The control technology of paint rheology is the key to the design of waterborne coatings. The rheological properties of waterborne paints are shown in Figure 1. When the water-based paint is sprayed, the viscosity of the water-based paint rapidly decreases under high shear force to ensure that the paint has a good micronization effect; when the shear force is eliminated, the high-viscosity state is rapidly restored, thereby ensuring that the metal pigment is good The directional effect and anti-sag performance. The biggest advantage of waterborne coatings compared to solvent-based coatings is low VOC emissions. 3 water-based paint process and equipment design need to pay attention to some of the issues The water-based paint coating process is basically the same as the solvent-based paint, but the equipment selection materials and process parameters need to be selected according to the characteristics of the water-based paint. The typical process is: 3.1 Pre-processing Before the steel cans are painted, all preparations for removing all kinds of dirt, degreasing, and covering certain types of chemical conversion coatings are collectively referred to as the surface treatment before painting. Pre-painting surface treatment technology is an important part of the coating technology. During the entire process, various fine chemical products such as cleaning agents, surface conditioners, phosphatizing agents, passivation agents, and oxidants are required. These chemical products are composed of Due to the complexity and large differences in performance, improper selection or use of various baths cannot be well controlled and managed, but adversely affect coating quality. Since water-based paints use water as a diluent, the surface tension of water is 72.6 dyn/cm, which is 2.5 times larger than that of common organic solvents and is 2.5 times that of common organic solvents used in paints. Therefore, it is difficult to infiltrate the substrate and shrinkage holes are easily generated. Surfactants are added to the formulation of waterborne coatings to reduce the surface tension and improve the wetting performance. On the other hand, when the pretreatment of the workpiece is performed, the surface treatment quality of the workpiece is required to be higher. 3.1.1 Degreasing The degree of degreasing on the surface of steel must be inspected and controlled in strict accordance with the requirements of GB/T 13312-1991. In this method, 2 drops (0.1 mL) of a standard G-type polar solution are dropped onto the surface of the test piece, and a 20 mm×40 mm covered area is immediately coated with a glass rod. A special type A oil test paper is tightly attached to the solution film. , Observe discoloration after 1 min. If the A-type oil test strips are uniform in colour and continuous and complete, they shall be qualified, otherwise they shall be unqualified. Regardless of the solvent-based coating or water-based coating, the quality of the degreasing quality will have a great impact on the quality of the coating film. However, for solvent-based coating spraying, when the surface of the workpiece is not completely degreasing, the coating film appearance Defects do not appear immediately, but for waterborne coatings, the surface is not completely degreasing, and it is difficult to form a complete film on the surface. Therefore, the quality of pretreatment is more important for water-based paint spraying. 3.1.2 Phosphating Phosphate film inspection should be carried out in strict accordance with GB6807-1986. It can be impregnated with 3% aqueous sodium chloride solution at 15-25°C, or with copper sulfate solution. Can also be painted after salt spray test to assess. Copper sulfate droplets were formulated as follows: CuSO4·5H2O was 41 g/L, NaCl was 35 g/L, and 0.1 mol/L HCl was 13 mL/L. The requirements for phosphate coatings for waterborne coatings are the same as those for solvent-based coatings. Phosphating films must be uniform and dense without fine dust. 3.2 Spray paint The general spray gun used for spraying water-based paints is the same as the solvent-based paints, but there are certain differences in the environmental conditions (mainly temperature, humidity) compared with the solvent-based paints. When the water-based paint is sprayed in the spray paint booth, the volumetric expansion of water into water vapor is 1,244 times, and the humidity in the paint spray booth can be instantly increased. When the humidity reaches 90% or more, the paint film coated on the paint will flow down. Therefore, spraying the water-based paint to control the humidity of the spray booth is very important, the temperature should also be maintained in the range of no sagging and runny, it is generally believed that the temperature of 15 ~ 30 °C, relative humidity of 60% ~ 80% is more appropriate. Since water is more corrosive than solvents, spray booths, especially circulating water treatment systems, are preferably made of stainless steel. The air supply in the painting room must have a proper temperature control and humidity control device. Domestic car painting booths can be used to regulate and regulate humidity in the winter, but there are few thermostats and humidity adjustments in the summer, because the required cooling capacity is too large, so there are few cold winds. Therefore, in the high-temperature and high-humidity areas, if water-based paints are used, central air-conditioning must be installed in the spray booth and cold air must be sent in summer to ensure the construction quality of water-based paints. The spraying environmental conditions for waterborne and solventborne coatings are shown in Figure 2. 3.3 Flash dry Flash drying is the leveling of the paint film after coating and the pre-evaporation process of the solvent (including water). Its purpose is to prevent the sudden appearance of the wet paint film containing a large amount of solvent or moisture (the water content of the water-based base paint is approximately 63%). Go to a higher temperature (>100°C) oven. Whether the flash drying process is set or not, the specific parameters of flash drying time and temperature are determined according to the performance of the water-based paint used, the quality requirements of the workpiece coating, and the temperature required by the drying oven. Under normal circumstances, the wet-on-wet process, oven drying temperature is higher (usually above 100 °C, higher than the boiling point of water), the film luster and appearance requirements are higher, the flash dry process should be set. The determination of the flash-drying time is mainly influenced by the chain speed for the production line. The flash drying time is short, the moisture and solvent in the coating do not volatilize in time, resulting in defects such as pinholes, tweezers and the like after baking at a high temperature; the flash drying time is long, the surface of the paint film is too dry, and the coating is prone to defects such as orange peel. It is necessary to reasonably select the flash-drying time, but at the same time it is necessary to increase the heating flash area. Otherwise, sagging, air bubbles and other quality problems will easily occur. 3.4 Drying Similar to the design principle of the spray booth, the high moisture content of the air in the drying chamber can also cause corrosion to the equipment. Therefore, the inner wall of the drying chamber must also be made of stainless steel. At the same time, the main body of the thinner in water-based paint is water, and the volatilization of water has a great relationship with the temperature and humidity of the spray booth. When the humidity is constant, as the temperature rises, the volatilization rate of the water increases; when the temperature is constant, the humidity increases, and the volatilization of water is hindered; when the relative humidity is too large, the water volatilizes very slowly, and the flow easily occurs during the construction process. Hanging paint film defects. Since the latent heat of evaporation of water is large (see Table 1), it is 5-7 times that of general solvents, and the heat capacity of the drying room should be increased moderately. At the same time, water evaporates more slowly than organic solvents, resulting in a longer drying time for water-based paints and an unreasonable increase in the temperature of the coating and the substrate. In waterborne coatings, except for the coating obtained by the electrophoretic coating method, the electroosmotic effect makes the moisture content in the wet coating film small, and can be directly subjected to high-temperature baking, and other water-based coating films with higher water content must rely on Drying and stepwise heating (incubate for a while under 100°C) will cause the moisture in the film to evaporate, and then it will rise to the process temperature for drying. Otherwise, it will cause paint film defects due to intense boiling of water at 100°C. The drying temperature and time curves of the typical thermal convection heating of waterborne and solvent-based paints are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. All of them have the experience that drying clothes on outdoor air outlets is quick and dry. Conversely, poor ventilation is slow or dry. The relative humidity of the air is high and it is also slow. This is also the principle of drying waterborne paints. Therefore, controlling the humidity of the air in the drying and drying room is very important for the drying time and effect. 3.5 Automatic spraying system When using a high-pressure airless spray process, it is basically the same as a solvent-based paint. However, if electrostatic spraying is used, because the main solvent of water-based paint is water, it has high conductivity. For example, if the solvent-based coating is used, an internal power-up type rotary cup is used, and high-voltage static electricity leaks from the paint delivery system. Therefore, the water-based paint is The initial application of the general use of external power type rotary cup. With the development of technology, the internal power type rotary cup has been used on the water-based paint spraying line. Before the spraying starts, the paint is sucked from the paint bucket to the reservoir and then disconnected from the main circulation loop. This will prevent high-voltage static electricity from leaking into the paint booth, affecting production and causing danger. 3.6 Transfer paint system The paint transfer system for solvent-borne paints can be made of carbon steel. Waterborne paints corrode due to the rust of metals due to water. Therefore, waterborne paint transfer systems must use stainless steel. Compared to solvent-based paints, water-based paint transfer systems need to focus on low shear stress control, stable flow, and avoid high pressure systems. High shear, high flow rates, and high pressures accelerate water-based paints. Aging directly affects the quality of spraying. For example, the back pressure valve and stirring paddle of the paint transfer system must be of a low shear force type. Otherwise, the emulsification performance of the waterborne resin will be impaired; the flow rate of the solvent-based paint in the circulation system is required to be 0.3~ 0.7m/s, while the flow rate of waterborne paint is required to be 0.15 to 0.40m/s. 4 Fire and Environmental Issues 4.1 Fire problems Water-based paint is non-combustible material, the solvent content accounts for 10% to 12%, does not contain benzene, xylene, etc., so fire extinguishing fire-fighting facilities and flammable gas alarm devices can be basically ignored when setting fire-fighting facilities. Place a general fire extinguisher next to the spray booth. However, the base resin of water-based paint is still a flammable substance. After the paint dries, there is still the possibility of ignition. Therefore, the accumulating paint in equipment rooms such as paint spray booths and ventilation ducts must be removed in time to prevent paint burning and fire. There are no national standards for the technical conditions of water-based paint fire-fighting facilities and equipment design requirements for waste gas treatment. It is recommended that countries or industries formulate corresponding standards as soon as possible. 4.2 Environmental issues After the use of water-based paint, the VOC exhaust emissions requirements can be met without additional equipment. However, the waste water generated needs to be treated in multiple stages so that the COD can meet the emission requirements and be discharged. 5 Economics of Waterborne Coatings The same performance of water-based paint, the unit price is higher than the solvent-based paint, but not too high. Taking a black acrylic enamel as an example, the unit price of the black acrylic enamel is 18 yuan/kg, the unit price of the solvent is 10 yuan/kg, and the unit price of an equivalent water-based topcoat is 22 yuan/kg, using water as the solvent, and the cost can be can be ignored. The paint consumption of a steel drum workpiece is: 0.2kg, 0.2kg solvent (dilution and cleaning) consumption: 0.2kg×1/3=0.067kg The cost of paint is 0.2kg×18yuan/kg+0.067kg×10yuan/kg=4.17yuan/piece Waterborne coating cost: 0.2kg×22yuan/kg=4.4yuan/piece Water-based paint spray booths, leveling rooms, and drying rooms are preferably made of stainless steel to prevent equipment corrosion caused by high humidity during construction. The cost of equipment can be increased by about 10% compared with solvent-based paint equipment. If the country or industry can issue fire-fighting and environmental protection facilities and equipment standards for water-based paints, replace the automatic fire-extinguishing system with ordinary fire-fighting facilities, and eliminate the installation of flammable gas alarm devices and exhaust gas treatment devices on the water-based paint spraying line, the investment in equipment will be reduced by 500,000 yuan. the above. In summary, the former is slightly higher than the latter in terms of use, material cost, and equipment investment, but if the water-based paint does not consider automatic fire extinguishing systems, combustible gas alarms, and exhaust gas treatment Devices, the two equipment investment is basically the same. At the same time, water-based paints are recyclable. According to the characteristics of the work-pieces, they can generally be recycled from 10% to 30%. If the environmental protection costs, the worker's operating environment is greatly improved, and occupational diseases are reduced, comprehensive factors such as environmental protection costs, use of the former, and material costs are also included. To be lower than the latter, waterborne coatings are worthy of generalization and application regardless of their economic or social benefits. 6 Conclusion The fundamental difference between solvent-based paints and water-based paints is that solvent-based paints use toxic, contaminated, and combustible organic solvents as the diluent, while water-based paints mainly use tap water as the diluent. Although the performance of waterborne coatings still needs improvement, replacing solvent-based coatings should be the trend. The conditions for the popularity of waterborne coatings have matured. In the coming years, waterborne coatings will have a great potential to replace solvent-borne coatings. It is very important to study the construction process of waterborne coatings. This article briefly discusses some issues that need attention in the spraying process and equipment design of waterborne coatings. The point of view is to use and for some waterborne coatings when designing waterborne coating spraying process. A summary of production units and some related technical data for reference by their counterparts in the related design. Hair Stylers,hot air styler,hair stylers for short hair,hair dryer and straightener set,mini hair straighteners,air hair styler Ningbo Meirou Electric Appliance Co.,Ltd. , https://www.mrhairstraightener.com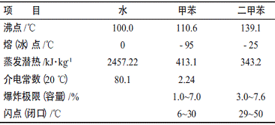
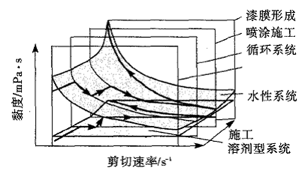
Fig. 1 Rheological properties of water-based paint
Pre-treatment [Upline → Pre-degreased → Degreasing → Wash 1 → Wash 2 → (Deionized water wash 1) → (Tune) → (Phosphate) → Wash 3 → Wash 4 → (Deionized water wash 2) → Manually blow water → Drying] → Painting → Leveling → Flash Drying → Drying → Cooling (Strong Cooling) → Offline 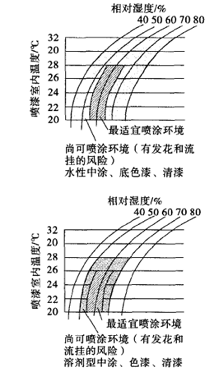
Fig. 2 Spray environmental conditions for waterborne and solventborne coatings 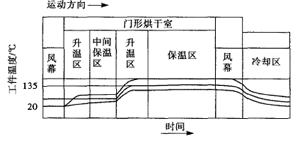
Figure 3 Curing (Drying) Curve of Waterborne Coatings 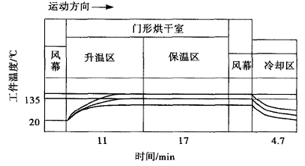
Figure 4 Curing (drying) curve of solvent-based paint
Problems Needing Attention in Spray Painting Process and Equipment Design of Waterborne Coatings