2. Results and Discussion 2.1 Analysis of Water Absorption of Degradation Films From the nature of the permeability of the material, the permeability mechanism of moisture permeability and air permeability is almost the same, so the permeability of the degradable film should also be higher than the permeability of the general plastic film. 2.3 Analysis of tensile properties of degraded films 2.4 Deformation film right angle tear strength analysis 2.5 Degradation Test Results and Analysis After 24 days of testing, it was observed that the transparency of the test film was higher than before the test, indicating that part of the starch in the film had been degraded. By calculation, the amount of CO2 released by the three degradation films in the soil buried environment of 24 days and 30°C has exceeded 40 mg, in which F1 = 44.83 mg, F2 = 48.62 mg, F3 = 47.87 mg, and the degradation rate is greater than 20%. . 3, the conclusion 1) Compared with general plastic film, starch-polyethylene biodegradable film is an environment-friendly plastic with easy degradation and little environmental pollution. At present, the starch content of the degradative films used in the market is above 40%, and some are as high as 80%. It is well known that the higher the starch content, the better the degradation performance of the film. Soil burial tests show that the degradation rate of the degradation film used in the test can reach more than 20% within 20-30 days. The degradation effect is still significant. 2) Compared with general plastic films, the physical properties such as water absorption and permeability of starch-polyethylene biodegradable films are higher than normal. Selecting a reasonable application for these performances is particularly important. If good permeability is not suitable for packaging with higher barrier properties, it can be studied in the application of modified atmosphere packaging. If the composite film or general-purpose plastic film is replaced with a degradable film, the water resistance is slightly reduced. However, from the viewpoint of environmental protection and ecological maintenance, this application should be acceptable when the requirements for use are satisfied. 3) Compared with general plastic film, the mechanical properties of starch-polyethylene biodegradable film are also ideal. In practical applications, it can withstand a certain load without damage, such as the degradable plastic bags used in many large-scale supermarkets. Requirements. At the same time, the study also found that the high heat seal strength of the degradable film, moderate friction coefficient, which are conducive to the production and application requirements of the packaging field. Although the starch-polyethylene biodegradable film still has some unsatisfactory places in its production and use, such as the price is higher than that of the general plastic film; the time-effect problem of degradation control and the evaluation problem need to be standardized and unified. Degradation of the polyethylene molecular skeleton during the degradation process is still relatively long, but degradable plastics as an ideal new technological approach to the treatment of plastic waste will be more satisfactory through the active development and applied research of scientists from various countries. The effect of the application in the packaging field will also shine. (Wen Tengjun Wang Gaosheng Cao Min Guo Yuhua Ji Hongwei Shao Wenquan)
We are manufacturer and supplier of stainless steel and aluminum alloy two materials Lemon Presser,Lemon Crusher,Squeezer For Lemon,Lemon Press Squeezer,Lemon Press. And we located in Jiangmen, Guangdong, China. If any interested, please contact us for free.
From Table 1, we can see starch at room temperature. The water absorption rate of polyethylene degradation film is higher than that of general plastic film, especially polyethylene film, and the main reason comes from the structure itself. During the processing of the starch-polyethylene degradation film, in order to effectively mix the starch and the polyethylene, in addition to adding an appropriate amount of the compatibilizer, it is necessary to add a plasticizer such as glycerin, sorbitol, etc. to properly paste the starch. The plasticization and plasticization improve the physical and chemical properties of starch and increase its dispersion uniformity in polyethylene. If the gelatinization is good, the plasticized starch granules will contain more polyhydroxy compounds, and its presence will directly lead to the water absorption rate of the degradable film is obviously higher than that of the general plastic film. 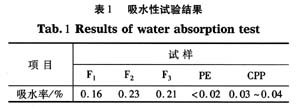
2.2 Moisture permeability analysis of degraded films
Table 2 shows that there is a large difference in the moisture permeability between the degradable film and the general film, and the main reason for this is due to the particularity of the internal structure of the material. In the starch-based ethylene biodegradable film, the distribution of the starch is not continuous, and its dispersion is also inhomogeneous. Most of the modified starch granules have irregular polygonal shapes. While satisfying the mechanical binding force of the reinforced starch and polyethylene interface, they actually form the basic “defects†of the structure, ie, the interface between the polyethylene and the starch exists. With tiny holes and gaps, it has less resistance to water vapor or other gases than general plastic films. As the test results show, the degradation of the test film for water vapor is much higher than the general plastic film. 

The results in Tables 3 and 4 show that both the tensile strength and the elongation at break of the degradable film can meet the requirements for use compared with the general plastic film, and the non-uniformity of the thickness of the degradable film has a great influence on the tensile strength. The starch-polyethylene biodegradable film is based on polyethylene and the starch is a disperse phase blending film. Although the chemically modified starch is effectively blended with the polyethylene, the monomer particles are easily dispersed in the polyethylene. The two interfaces are tightly combined by physical and chemical interactions, but the lack of continuity and inhomogeneity of the starch in the blend film still leaves a monomer "defect" in the film structure, and a "defective effect" when the film is stretched. The two interfaces in the direction of force are separated to form cavities and expand in the horizontal direction. Therefore, the appearance of local stress concentration phenomenon will make the tensile properties of biodegradable films worse than that of polyethylene films under the same conditions. 
The test data in Table 5 also show that the degraded film has a right-angled tear strength due to structural “defects†that is also less than that of the general plastic film.
Lemon Presser,Lemon Crusher,Squeezer For Lemon,Lemon Press Squeezer,Lemon Press
Jiangmen Xinhui Zhancha Metal Products Co,. Ltd. , https://www.zckitchenware.com